Metadata example is everywhere. Be it the smallest decision to buy a dress or a big decision to buy a house, the smart consumer of today will do all the research before making a decision. This means that the brands need to be on their toes to make sure that the data associated with their content is verified.
It is important to know how the data was collected. When was it collected? What were the inputs to data collection methodology? What was the geographical area of the data collected? What variables were used, and how do they influence the answers? Which software was used for analysis, and what was its calibration for data collection? Are some of the questions that Metadata example answers in the form of a data set.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Metadata?
The term metadata became popular in the 1990s. It was used to describe the online resources or create libraries. Today metadata is everywhere, in every image you take or download, an email you write, the website you sign up for, or order something online.
Definition of metadata: It is the information that describes and explains data. In simpler words, meta data is “data about data.” A metadata associated with a file will contain its details, such as source, history, versions, type, format, owner, etc. It is a simple and well-structured contextual description about data, making it easier to identify, understand, and manage.
Metadata is popularly used as a blueprint or summary of a data set containing critical details such as content’s origin, purpose, location, format, and usage to track, classify, and analyze. Metadata does not have any content of its own, but it is needed to ensure the relevance of the picture or text and that it is compliant with the data regulations. For example, the metadata of an image that you have just clicked will contain all the information about its size, device, location, resolution, time of creation, color, and depth.
Types of Metadata
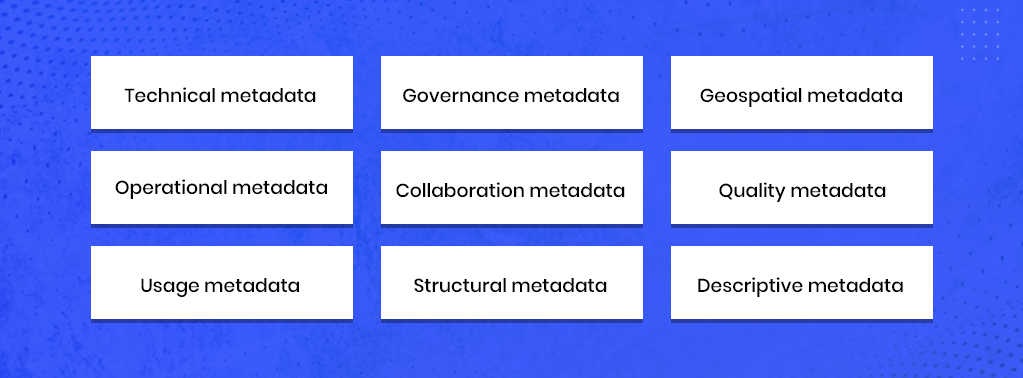
- Metadata is classified in many different forms. Metadata can be classified on the basis of its functionality or the sources. The common types of Metadata Example classifications are
- Technical Metadata, which includes rows or column counts, data types, etc., provides details about how data is created, stored, and delivered.
- Governance Metadata that has ownership information, data classification, governance terms.
- Geospatial Metadata that gives geographic and spatial information such as longitude, latitude, map projections, etc.
- Operational Metadata that stores dependencies, codes, and runtimes.
- Collaboration metadata shows comments and discussions about the file.
- Quality, which indicates the freshness of the dataset, its status, run, etc.
- Usage, which indicates top users, view count, popularity, and so much more.
- Structural Metadata stores information about how the data is organized and interrelated. A metadata example of this kind is the table of contents in a book.
- Descriptive Metadata indicates the data source.
Preservation Metadata: Necessary for managing and protecting the digital asset and helps maintain the authenticity of the product.
Administrative Metadata: Includes the rights, access control, permissions, creation data, intellectual property, etc., of the digital file.
Provenance Metadata : Used to track the origin and history of the data and helps verify the modifications and version histories and chain of custody.
Metadata: Also classified as active and passive metadata depending on how the Metadata Example is collected and managed.
Metadata Examples
Metadata in a Photograph
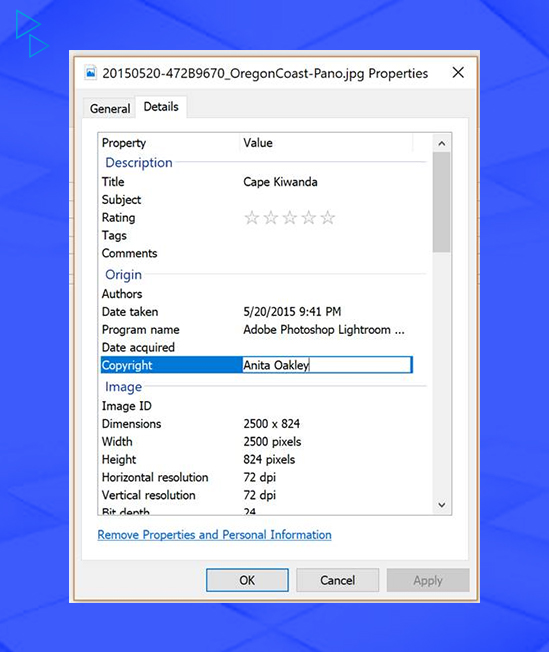
- Descriptive metadata: Filename, title, description, and tags.
- Technical Metadata: File size, resolution, and formats.
- Administrative Metadata: Creation data, copyright information, or ownership.
- It will also contain other types of information, such as the make of the camera, the lens used, and the time at which the picture was taken. EXIF, GPS location color profiles, etc.
Similarly,
Digital libraries use metadata to categorize or organize their collections to identify, locate, and classify the library’s collection.
Metadata Examples : Digital documents are in the form of title, author, creation date, file size, history, and keywords.
Webpage Metadata: Comprises of title tags, meta descriptions, keywords, and alt text for images. In multimedia files, you will see Metadata Example listing artist name, album titles, genre, duration, bitrate, etc.
A Database Metadata: example listing of column names, data type, and relationships between tables. E-commerce products display metadata as product name, price, category, user reviews, and dimensions of the product.
Metadata for a document contains details like author, size, and title, helping them be categorized accurately. It also makes tracking the changes easy.
A spreadsheet file’s metadata will contain number of rows or columns, data types, column statistics, validation rules, data owner, creation date, comments, and information about the latest changes. Social metadata, for example Facebook metadata contains information like title of the post, description of the post, featured image, URL, and name of the website.
Benefits of Using Metadata
Metadata offers technical insights about data. The right context is essential in using the data, and metadata helps by making the data discoverable, accessible, trustworthy, and valuable. Without Metadata Example, it will be impossible to find anything in the digital data burdened world.
Here are some benefits of metadata that make it indispensable:
It makes the Data Discoverable.
For websites, databases, and users, metadata plays the vital role in improving the functionality of the systems. Helps organize and retrieve information easily. It improves searchability and SEO, enabling users to find the items that interest them, record the information, and share that information. Reduces time spent in data discoverability.
Makes Data Organization Simpler
Having Metadata Example enhances data organization by making it categorizable and searchable, thus streamlining the workflow.
Efficient Data Management
Metadata enables the user to have a comprehensive, up-to-date view of the data, such as lineage, quality, context, etc., to help keep track of origin, history, ownership, versioning, etc. that is crucial to ensure compliance and governance.
Ensures Better Interoperability and Collaboration
The tech stack shares the standardized information across systems, platforms, and tools, making it easier to share and understand data. Interoperable systems.
Better Context and Insights for Decision Making
Metadata Example gives structured information about data, purpose, sources, and relevance in an organized manner, making it easy to compare and understand. This aids in informed decision-making by both human and AI.
Some use Cases of Metadata
Metadata has many functions, including organization and description, facilitating search and retrieval, ensuring utilization and preservation, and enables ethical reuse and multi-versioning and facilitates collaboration
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Using right Metadata Example like descriptions, alt-tags, and keywords, to drive in more traffic and boost the search engine rankings.
Data Governance
Metadata is used by enterprises to maintain and monitor data compliance by monitoring usage logs and access controls.
E-commerce Platforms
Metadata boosts shopping experience by letting online stores give users the facility to filter the products by price, brand, ratings, and more.
Cloud Data Management
With cloud services rising in popularity, contexts given by metadata help Google Drive or Dropbox use it for tracking document versions, sharing permissions, and authorships.
Healthcare Industries
There are two ways metadata is used in healthcare industries. Metadata of research databases plays an instrumental role in storing data, experiment details, measurement units, methods used to boost collaboration and ensure reproducibility. Metadata is also used to maintain the electronic health records helping maintain a database of patient information, medical history, and treatment plans.
Final Thoughts
Metadata brings context to raw data, making it an indispensable part of data organization and digital management. Metadata facilitates efficient data handling and decision making, thus offering deep insights into data, and ensuring usability, discoverability, and compliance in all fields.
Read Also: How to Incorporate Customer Engagement into your Digital Transformation Strategy?
Written By – Amit Bhateja
Amit Bhateja is the co-founder of enrcloud and helping brands and Unicorns from the last 15+ years and overachieve their Engagement and Retention goals. He is passionate about solving customer problems with modern technology, new age solutions, and consultancy approach. Besides Building ENR, He enjoys reading books, spending time with his family and Teammates, traveling, meeting new people, learning new things, and love to close the business deals.





